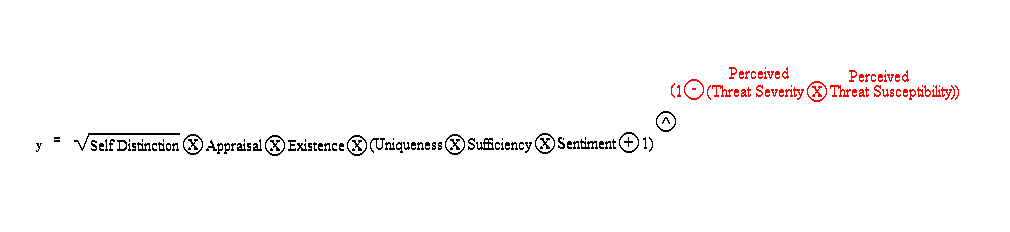Threat Severity and Threat Susceptibility, along with Response Efficacy and Self Efficacy, are concepts adapted from theories of health risk messages and fear appeals (e.g., Dr. R.W. Roger’s Protection Motivation Model and Albert Bandura’s conception of Efficacy).
Informational Links
- Consumer Health Informatics Research Resource: Perceived Severity, Perceived Susceptibility
- Wikipedia Roger’s Protection Motivation Theory
The application of threat in Affect Engineering, however, is centered on the relationship between a threat and a particular entity being valued by the individual for fulfilling a purpose. Affect Engineering also makes use of contingency theory. For instance, in a situation where the contingency between one event, A, and another event, B, are perfectly negative, the presence of A would signal the absence of B. Though I describe four different forms for both the Avoidance of Pain and Pursuit of Pleasure functions in the book, making a grand total of eight where the contingency between A and B is positive in four and negative in the other four, only two forms out of the eight are needed to model all the emotions. While the other six forms are useful for studying semantics and different ways of saying the same thing, in the majority of my examples I use a contingency between A and B that is negative and will do so here.
In short, Threat Severity is an assessment of how dangerous a harm is. In the context of the equation, this could be the extent to which an entity is destroyed, damaged, made unusable, or access to it is denied.
Threat Susceptibility is an assessment of how likely the threat of harm will occur.
The implementation of Threat Severity and Threat Susceptibility is different for the two types of equations.
Perceived Threat Severity and Threat Susceptibility are modeled above as an exponent in the Avoidance of Pain function. The values for each of the two variables may be between zero and one. If unchecked by attentional processes or efficacy, a threat of harm to a valued entity would be expected to cause an individual to reassess and elevate the entity’s value continuously. As Threat Severity approaches one (e.g., total destruction) and Threat Susceptibility approaches one (100% likelihood) the valuation of the entity (Emotional Units and anxiety invested in the entity) approaches positive infinity over time. Although multiplication is used to describe the relationship between Threat Severity and Threat Susceptibility above, they may be decoupled with addition in a similar fashion to the Utility variables in the base of the equation. The Appraisal variable in the above formula would be positive one (+1).
Perceived Threat Severity and Threat Susceptibility are modeled above as an exponent in the Pursuit of Pleasure function. The values for each of the two variables may be between zero and one. If unchecked by efficacy or inattention in this case, a threat of harm to a valued entity would be expected to cause an individual to reassess and elevate the entity’s value continuously. As Threat Severity approaches one (e.g., total destruction) and Threat Susceptibility approaches one (100% likelihood) the valuation of the entity (negative Emotional Units and negative anxiety invested in the entity) approaches its Existential value of negative one. The different setup for the Pursuit of Pleasure function reflects the notion that a threat of harm to an entity that is already in adequate supply (i.e., acquiring more of it will lead away from equilibrium and homeostasis) will simply lead to a loss in pleasure for the specific purpose, as opposed to an increase pain if the entity were needed to achieve equilibrium. Although multiplication is used to describe the relationship between Threat Severity and Threat Susceptibility above, they may be decoupled with addition in a similar fashion to the Utility variables in the base of the equation. The Appraisal variable in the above formula would be negative one (-1).
In Affect Engineering, the magnitude and type of a particular emotion felt is gauged by the slope a function, hence, by finding the derivative of a function at a particular point in time. Threat and Efficacy, therefore, are modeled to play a significant role in the amplification and de-amplification of an entity’s original valuation, thus leading to the formation different outcomes. Their roles, however, can be reduced, increased, or held constant by attention and reasoning, as will be shown.