An Appraisal in the context of the equation concerns the individual’s assessment of whether an entity’s further acquisition will lead toward the restoration of equilibrium between a purpose and that purpose’s complement. Though an individual gives an entity a value judgment for both a purpose and the complement to the purpose (e.g., to hydrate and to not hydrate), if the entity is useful for one purpose, then its value for the complementary purpose will become negligible, that is, remain at or near its Existential value. An object cannot be useful (i.e., have a maximum Utility value) for both a purpose and that purpose’s complement without violating the 1:1:1:1 ratio. In cases where it appears that an object does seem to be both useful for doing something and not doing something, the object is likely being used in a different manner and hence, for a different purpose.
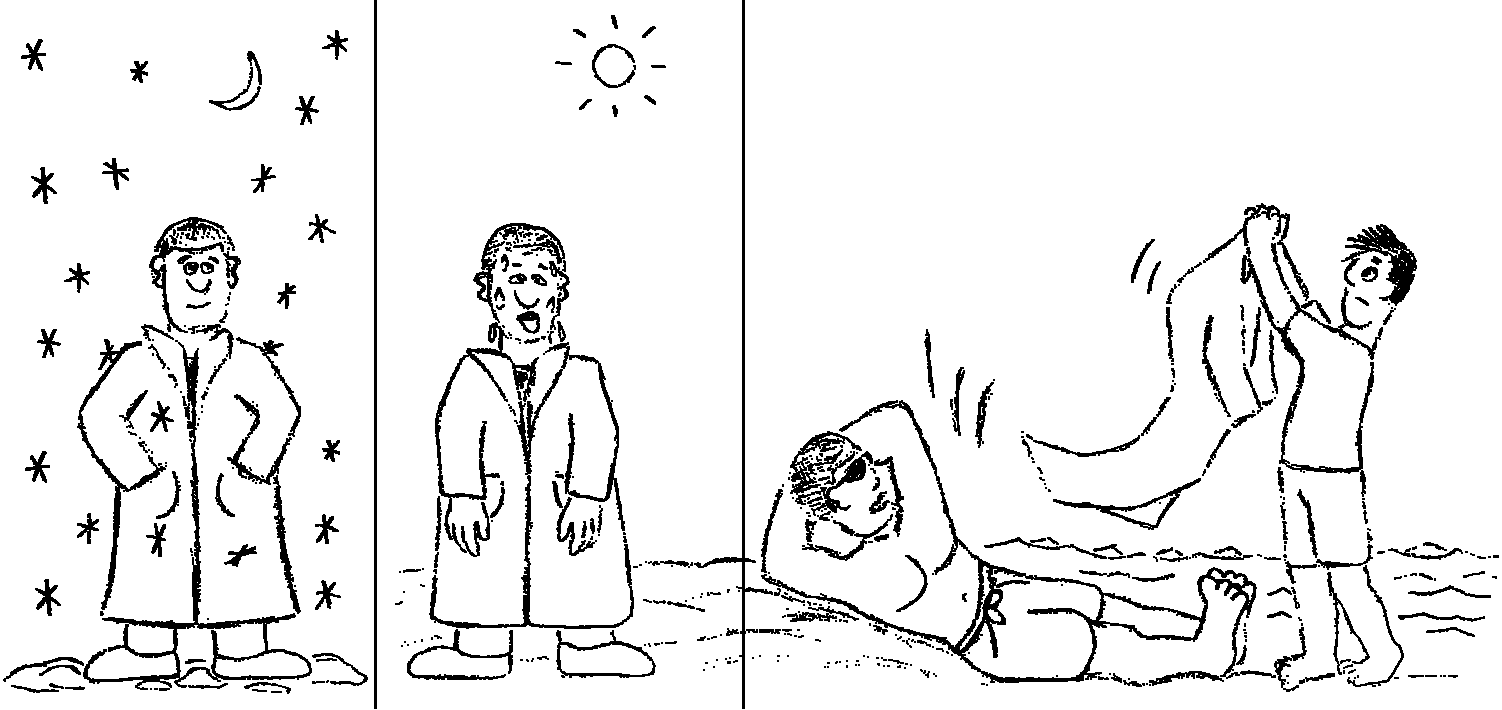
Figure 6.15, from Affect Engineering: A Unified Field Theory of Emotion, p. 102. An entity cannot be both useful for a purpose and not useful to that same purpose without violating the 1:1:1:1 ratio. In the first two images (left and center) the coat’s value is being considered for the purpose of wearing clothing to keep warm versus not keeping warm. In the third case (right) the coat’s value is being considered for the purpose of serving as a fan to keep cool or not to keep cool. Maintaining that there are four purposes in play, and not two, upholds the 1:1:1:1 ratio.
The restoration of equilibrium between a purpose and its complementary purpose is synonymous to achieving homeostasis. Though homeostasis is generally what people seek, as survival necessitates maintaining balance, the functions in Affect Engineering are also capable of modeling affect that arises when homeostasis is not the desired aim. Some circumstances where homeostasis is not the desired aim may arise from martyrdom, altruistic suicide, or instances when an individual pushes his or her body beyond its physical limits.
Appraisal, as a variable, is restricted to either positive one (+1) or negative one (-1), and is a coefficient alongside Existence.
y = Appraised Value Judgment = Appraisal × Existence × ( Sufficiency × Uniqueness × Sentiment + 1 )
Avoidance of Pain Functions: Anxiety, Pain, and Negative Affect
Where the Appraisal value is positive one (+1), it signifies that acquisition of the entity will lead toward a restoration of equilibrium between a purpose and its complementary purpose. Hence, the entity is in short supply and acquiring it will restore balance. This holds true so long as the entity’s absolute Utility value for the purpose being considered is greater than its absolute Utility value for the complementary purpose. Additionally, if the Appraisal value is positive one (+1), then the function is modeling anxiety invested in an entity. These functions are designated Avoidance of Pain Functions, as they generally concern themselves with the minimization of anxiety invested, the reduction of negative affect, and a restoration of equilibrium so that emotional resources can be freed up to invest elsewhere.
Avoidance of Pain Function thus far,
y = Appraised Value Judgment = ( +1 ) × Existence × ( Sufficiency × Uniqueness × Sentiment + 1 )
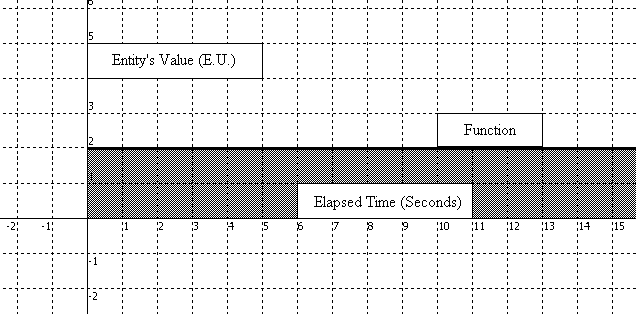
The above is an Avoidance of Pain Function with all Utility variables maxed at one. The shaded region represents the Emotional Units (y-value) invested in an entity toward the fulfillment of a purpose over time (x-value). The shaded area is anxiety invested in an entity. The terms anxiety, pain, and negative affect may be used interchangeably and are all represented by positive Emotional Units invested in an entity, more specifically, when the function is above the x-axis.
Pursuit of Pleasure Function: Negative Anxiety, Pleasure, Positive Affect
Where the Appraisal value is negative one (-1), it signifies that acquisition of the entity will lead away from a restoration of equilibrium between a purpose and its complementary purpose. Hence, the entity is already in ample supply and acquiring more of it will further upset balance. Like the Avoidance of Pain function, this holds true so long as the entity’s absolute Utility value for the purpose being considered is greater than its absolute Utility value for the complementary purpose. Additionally, if the Appraisal value is negative one (-1), then the function is modeling negative anxiety invested in an entity. Negative anxiety is a term invented by the author and quite literally is the opposite of anxiety. These functions are designated as Pursuit of Pleasure Functions, as they generally concern themselves with the maximization of negative anxiety invested, and the amplification of positive affect at the expense of equilibrium.
Notwithstanding, the restoration of equilibrium between the original purpose and its complement does become a concern when other purposes begin to be neglected and are adversely jeopardized by fulfilling the original purpose. In this manner, the complement to the original purpose may become associated or linked to other purposes that can not by achieved while the individual is pursuing the original.
Pursuit of Pleasure Function thus far,
y = Appraised Value Judgment = ( -1 ) × Existence × ( Sufficiency × Uniqueness × Sentiment + 1 )
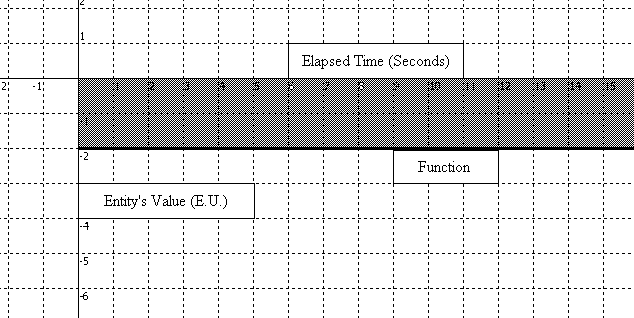
The above is a Pursuit of Pleasure Function with all Utility variables maxed at one. The shaded region represents the Emotional Units (y-value) invested in an entity toward the fulfillment of a purpose over time (x-value). The shaded area is negative anxiety invested in an entity. The terms negative anxiety, pleasure, and positive affect may be used interchangeably and are all represented by negative Emotional Units invested in an entity, more specifically, when the function is below the x-axis.


